| Project name | Fused Glass Deposition Modelling on Flat Glass: Investigations of process-structure-properties and feasibility of novel glass joints |
|---|---|
| Acronym | FGDM |
| Project partner |
|
| Grantor | Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft – DFG |
| Duration | 04.21 – 03.25 |
| Project content |
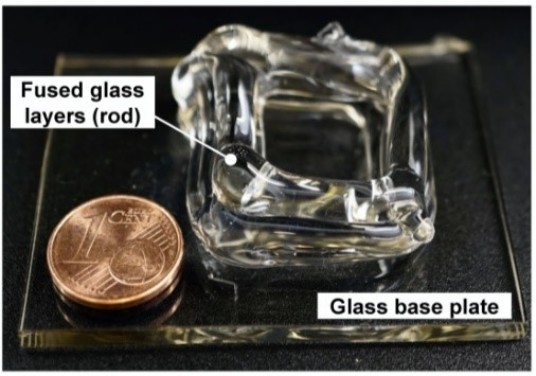
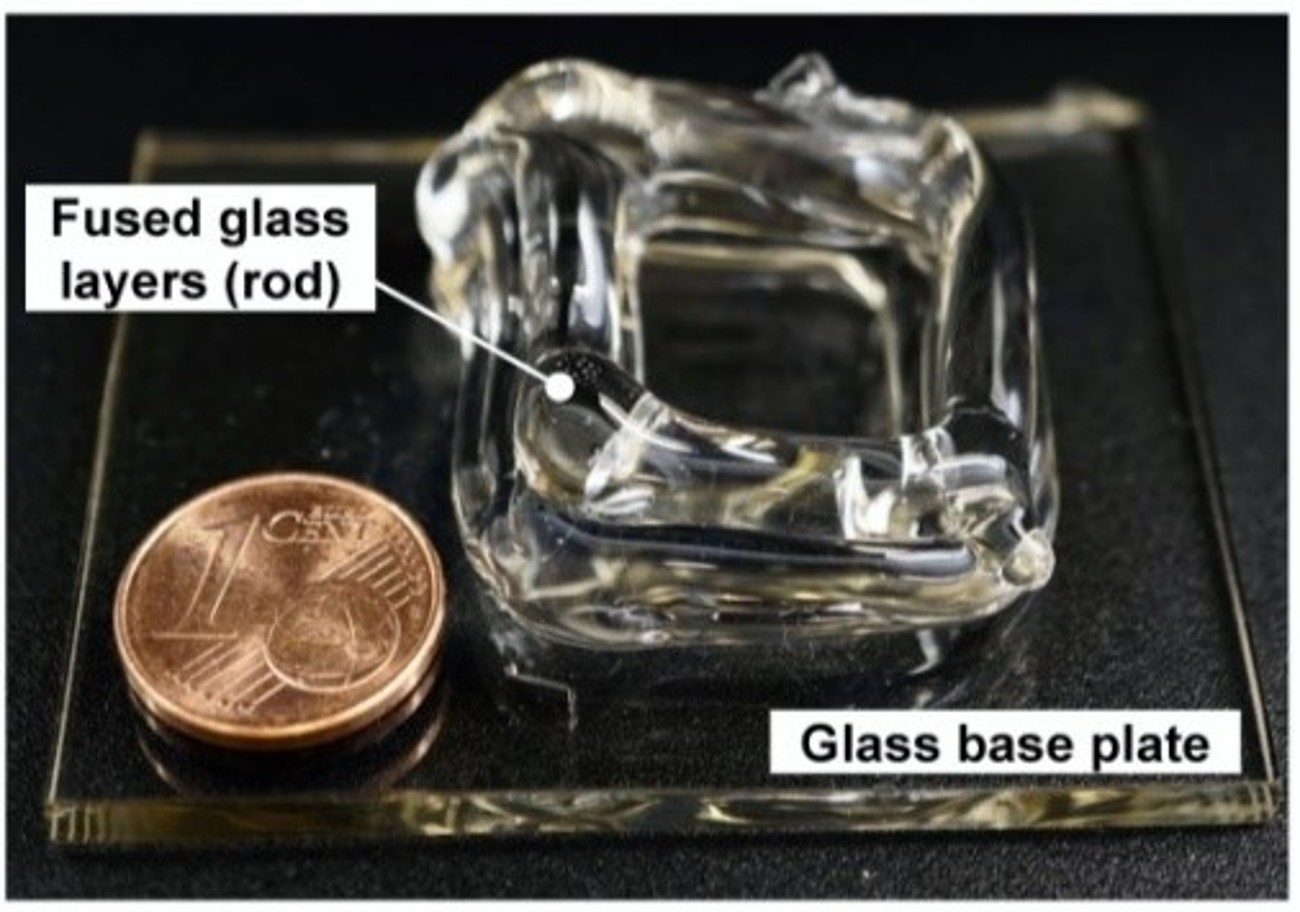
Additive manufacturing (AM) of metal and plastic components has garnered significant global attention in recent years, becoming a state-of-the-art technology across various industries. However, the additive manufacturing of glass is still in its nascent research phase. This technology could unlock new possibilities in multiple sectors for custom designs, such as construction, façades, furniture, and automotive. AM technology could enable homogeneous, transparent, and custom glass joints and reinforcements on flat glass. Additionally, it allows for creating a joint between fused glass and flat glass without the need for boreholes or adhesives. The vision includes façade glazing up to dimensions of 3.25 x 20 meters that could be attached to a substructure using printed glass joints and locally reinforcing the flat glass. Though some research projects have ventured into additive manufacturing of individual glass components, they have yet to address the joining process among fused glass layers and flat glass or larger glass structures. The AM of glass on flat glass is seen as a promising yet challenging idea. The successful joining of glasses mainly depends on the glass viscosity, joining time, and temperature conditions. Other parameters include heat quantities, geometry of the joining partners, thermal expansion behavior, and residual stresses generated. The research project aims to develop a fundamental understanding of the integrated joining process and identify potential structural applications for novel glass joints. Challenges include managing temperature fields and optimizing relevant parameters to achieve homogeneous and reproducible joints on flat glass. |
Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
FGDM
Fused Glass Deposition Modelling on Flat Glass: Investigations of process-structure-properties and feasibility of novel glass joints
FGDM
Fused Glass Deposition Modelling on Flat Glass: Investigations of process-structure-properties and feasibility of novel glass joints
Research project MPA